THERMOCYCLER (PCR Machine)
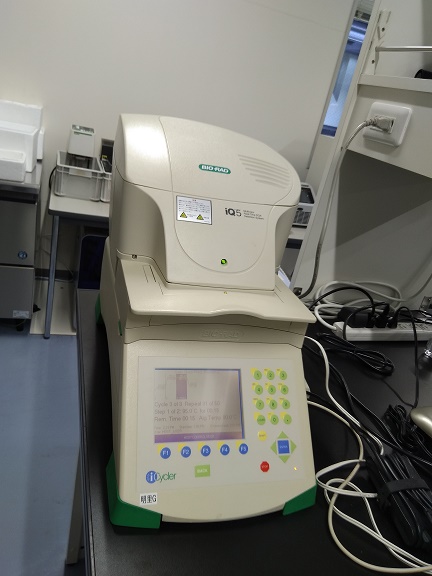
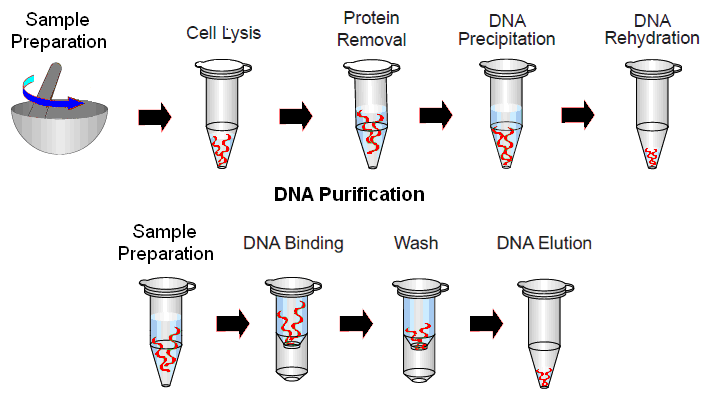
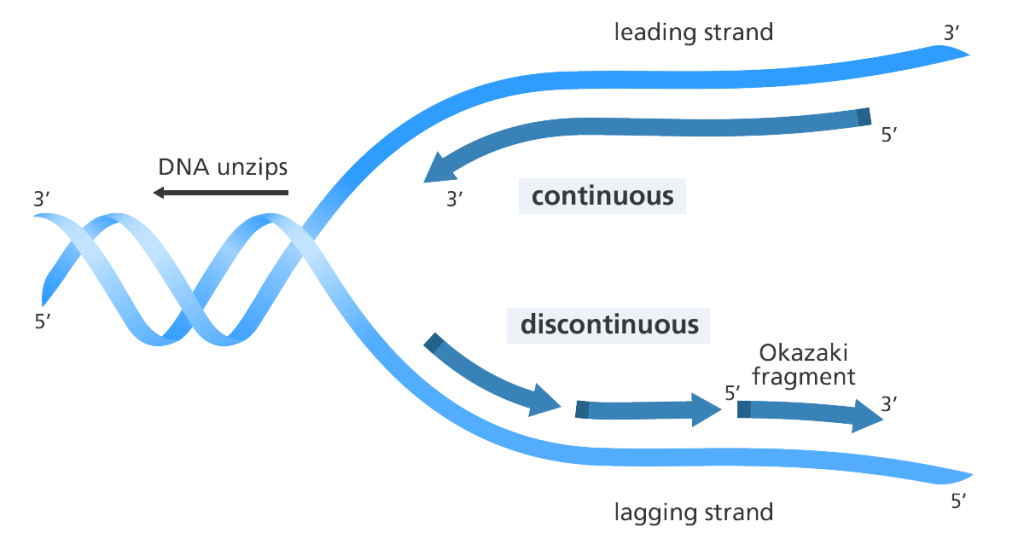
Thermocycler or thermal cycler is a piece of equipment is used for the copying or amplification of specific sequences of nucleotides through a controlled timing and temperature regulation. It is an important tool in the molecular biology laboratory. Thermocycler allows reaction mixtures in specialized tubes known as Eppendorf tubes (PCR tubes) to be heated and […]
THERMOCYCLER (PCR Machine) Read More »
Biotechnology, Molecular Microbiology, Techniques in Microbiology Lab