Are you looking for more information about Antibiotic Resistance or antimicrobial resistance (AMR)? Do you […]
Tag: antibiotics
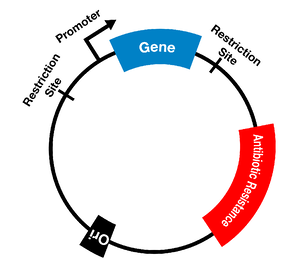
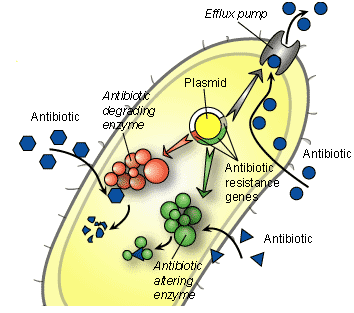
TYPES OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
Bacteria have evolved to survive in diverse environments. They survive exposure to harsh chemicals including […]
BRIEF HISTORY OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
Antimicrobial agents, particularly antibiotics are the most significant class of pharmaceuticals and are one of […]
HISTORY OF ANTIBIOTICS – a synopsis on how it all started
Over the past 70 years, antibiotics have saved countless number of lives across the globe […]
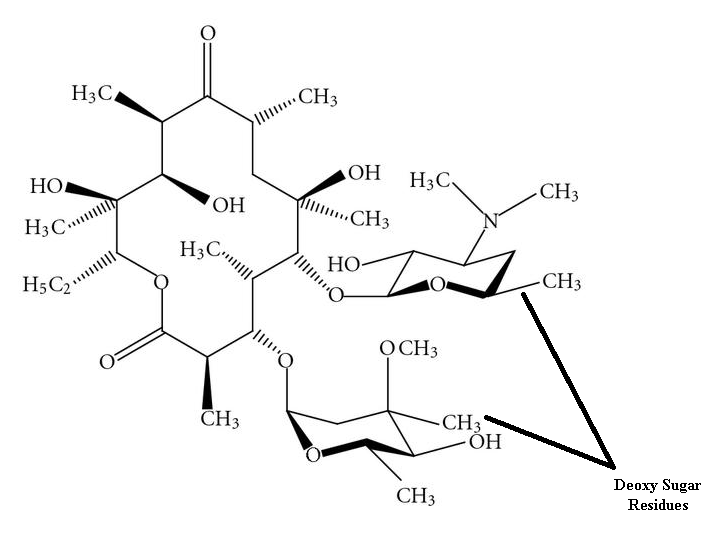
ERYTHROMYCIN
Erythromycin is a protein synthesis inhibitor that binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit of the […]
CHARACTERISTICS/FEATURES OF ANTIBIOTICS
Antibiotics including antibacterial agents, antiviral agents, antiprotozoal agents, and antifungal agents have some specific characteristics […]
ALEXANDER FLEMMING (1881-1955)
Alexander Flemming, a Scottish born physician who spent most of his time studying bacteria discovered […]
SPECTRUM OF ACTIVITY OF ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS
The growth of pathogenic microorganisms is usually accompanied by the synthesis of new molecules including […]
Overview of antimicrobial agents (antibiotics)
Ever since their discovery some decadesago, antimicrobial agents particularly antibiotics have saved mankind from the […]
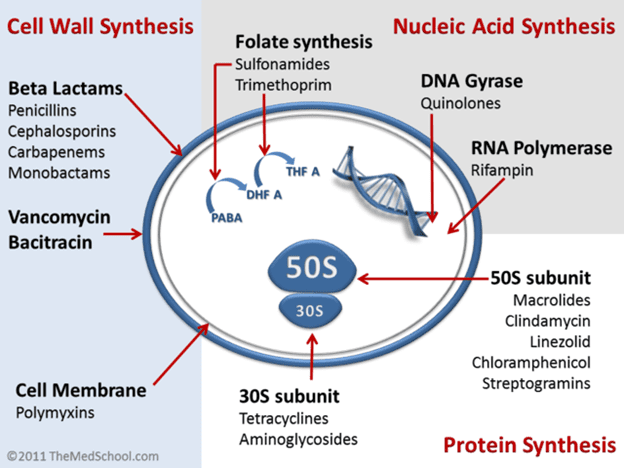
CLASSES OF ANTIBIOTICS
There are several classification/types of antibiotics today, which is based on bacterial spectrum of activity […]
SOURCES OF ANTIBIOTICS
Before the advent of conventional medicine used in clinical medicine today for the treatment of […]
BRIEF HISTORY OF ANTIBIOTICS
Antibiotic history dates back to 1928 when Sir Alexander Fleming discovered the antibacterial effects of […]
DEFINITION OF AN ANTIBIOTIC
There is no consensus to the definition of antibiotics. But it is very important that […]
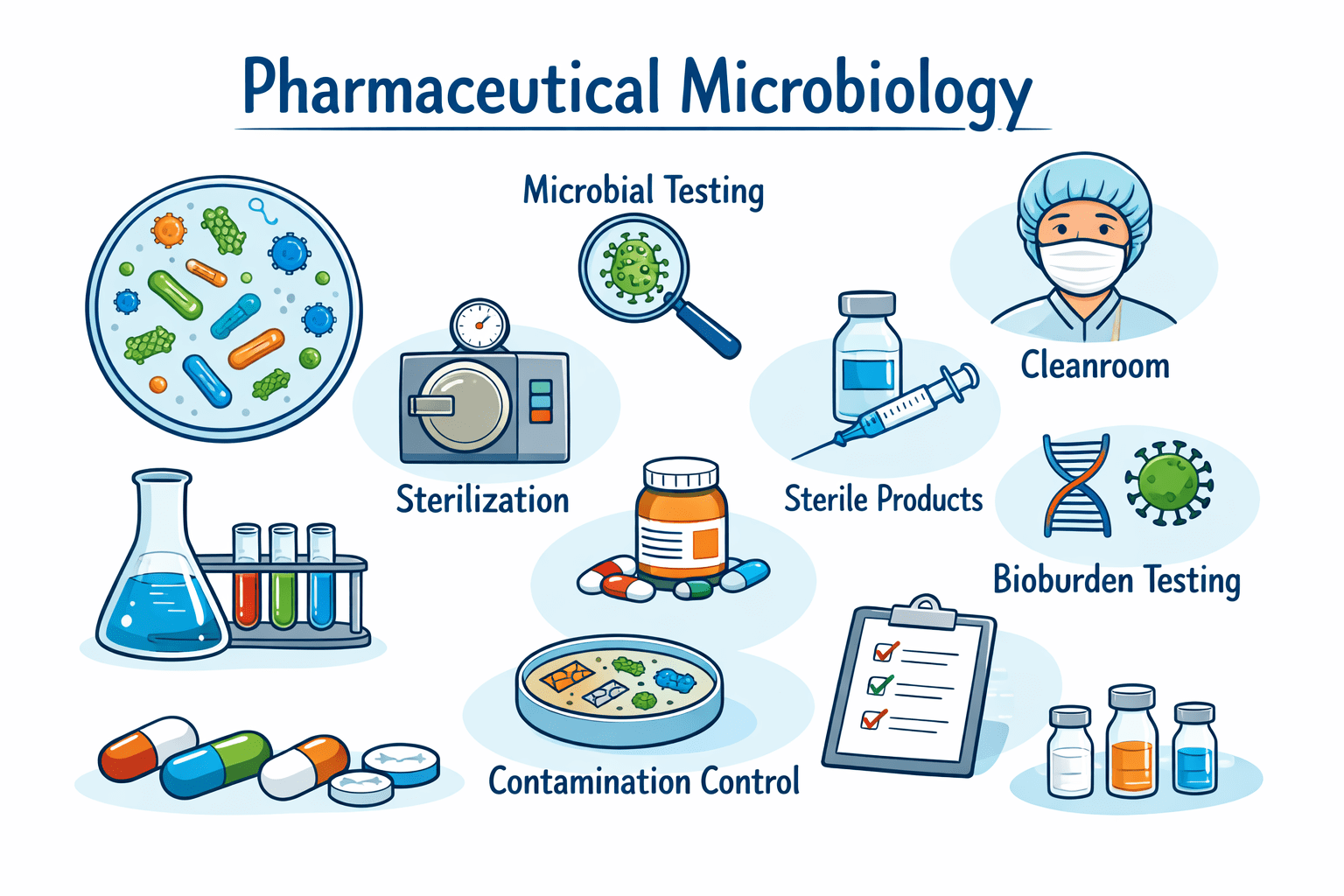
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Microbiology
Pharmaceutical microbiology is the branch of microbiology that focuses on all aspects of pharmacy especially […]