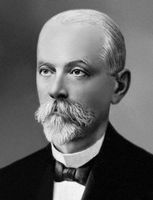SERGEI WINOGRADSKY (1856-1953)
Sergei Winogradsky was a Ukrainian-Russian microbiologist, ecologist and soil scientist who was among the first to delve into a different area of microbiology that involved the investigation of microbes in the environment that did not cause disease. Winogradsky pioneered the concept of bacteria (like nitrifying and purple-sulphur bacteria) that cycle nitrogen and sulphur compounds in […]
SERGEI WINOGRADSKY (1856-1953) Read More »
General Microbiology