MICROBIOTA (NORMAL MICROFLORA) OF LIVING ORGANISMS
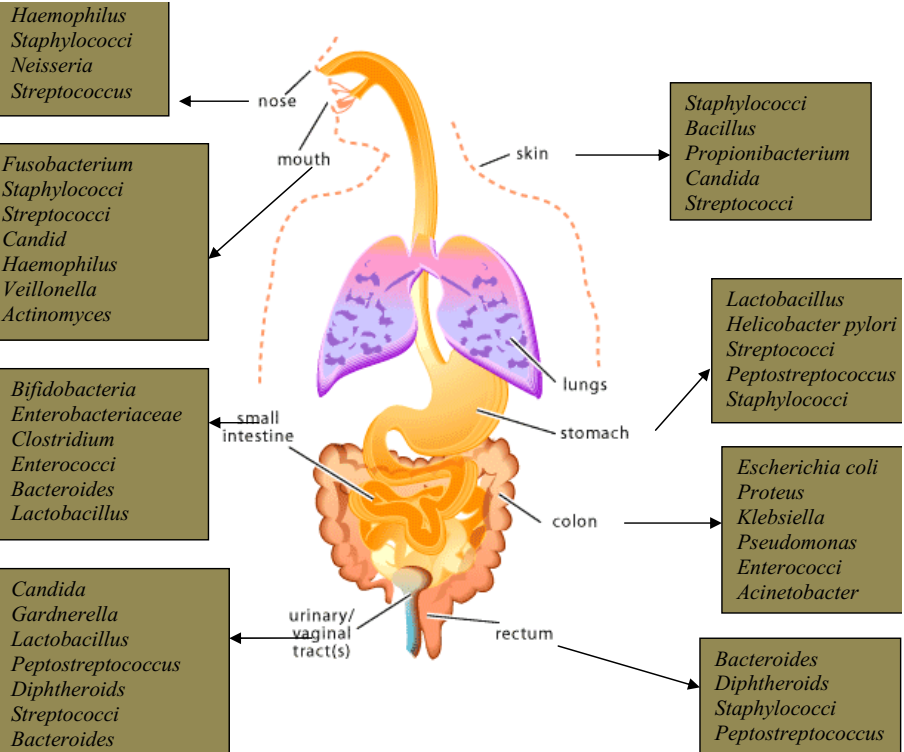
Microbiota which can also be called normal microflora is the totality of microorganisms that are inherently present in a particular environment, body or location at every specific point of time. Mycoflora are fungal organisms that live in particular sites of the body without causing infection or disease. Microbiota goes into competition with pathogens on and […]
MICROBIOTA (NORMAL MICROFLORA) OF LIVING ORGANISMS Read More »
Bacteriology, Medical Microbiology