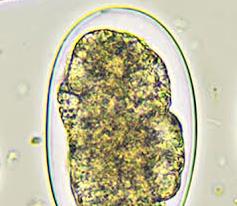
BLOOD CULTURE TECHNIQUE
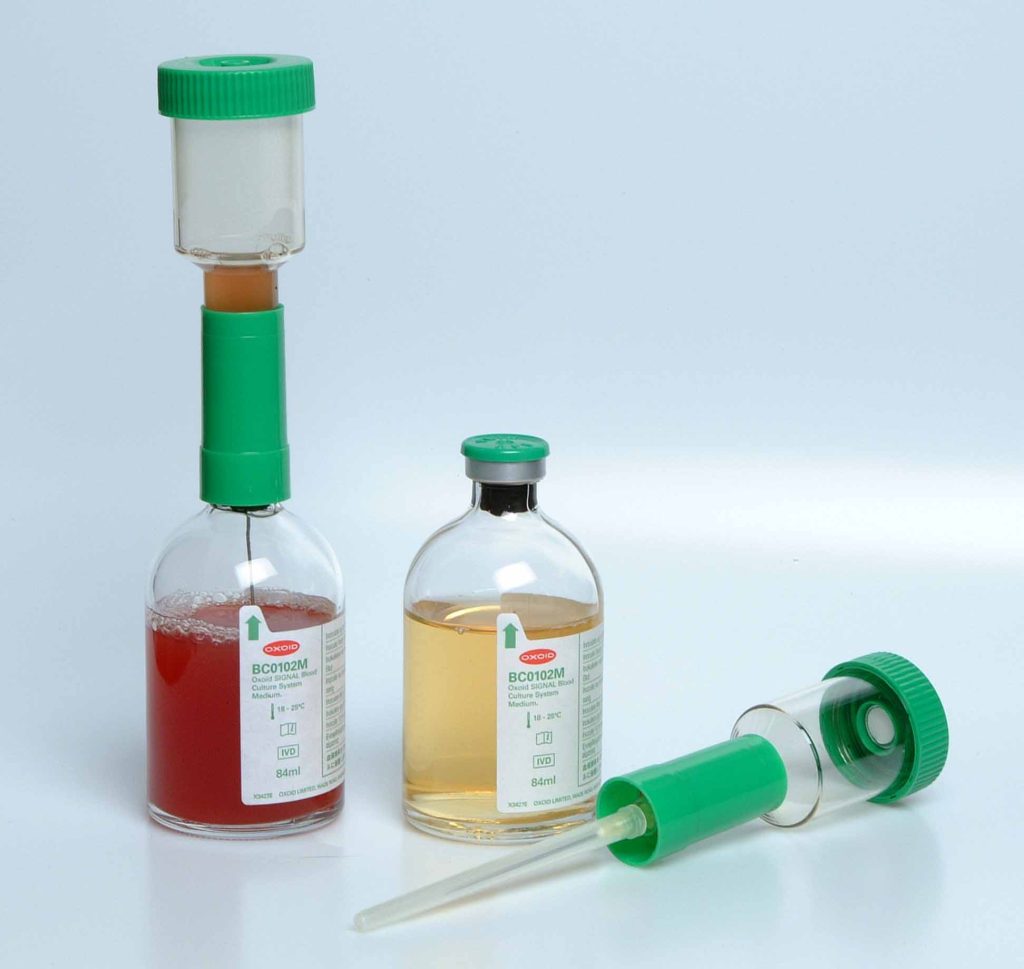
Blood culture is the most important diagnostic method for detecting and diagnosing bacteraemia (presence of bacteria in blood) and fungimia (i.e. presence of pathogenic fungi in blood) in the clinical microbiology laboratory. Blood specimen required for blood culture technique should be collected from the patient prior to antibiotic therapy in order to increase the sensitivity […]
BLOOD CULTURE TECHNIQUE Read More »
Microbe Lab, Techniques in Microbiology Lab