CLASSIFICATION OF MUTATION BY THEIR EFFECTS ON THE DNA MOLECULE
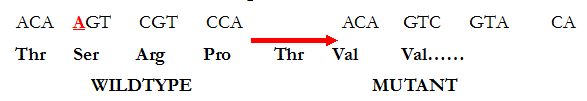
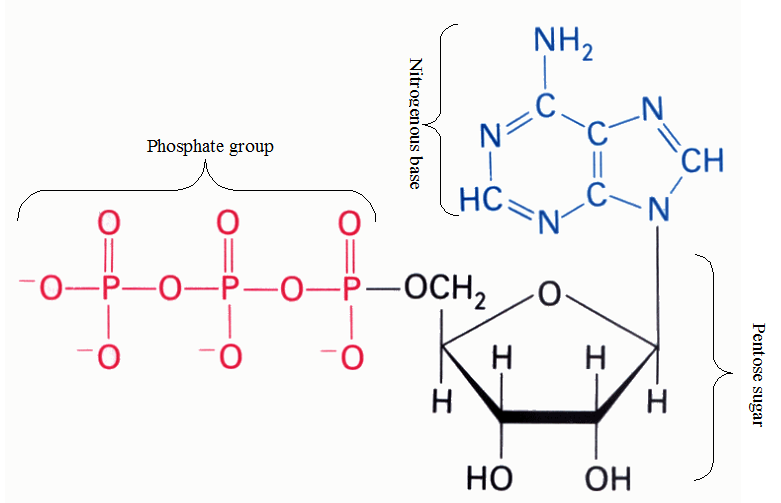
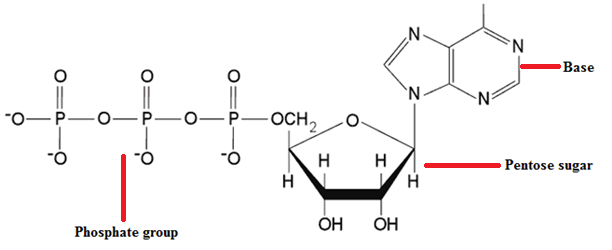
Based on their effects on the structural integrity of the DNA molecule, mutations can be classified as substitution, insertion, deletion, inversion, reciprocal translocation and chromosomal rearrangements. SUBSTITUTION (BASE-PAIR SUBSTITUTION) Substitution literally means the act of replacing one thing with another. When base substitution as a type of mutation occurs during DNA replication, a single base […]
CLASSIFICATION OF MUTATION BY THEIR EFFECTS ON THE DNA MOLECULE Read More »
Biotechnology