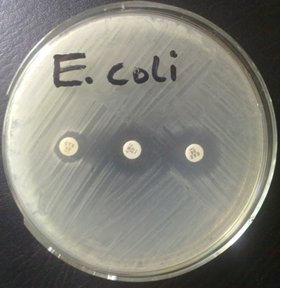
What does it mean to be ESBL positive? Learn how to detect these antibiotic-resistant bacteria […]
Tag: ESBL
What are ESBLs?
ESBLs (extended spectrum beta-lactamases) are enzymes that mediate resistance to extended-spectrum (third generation) cephalosporins (e.g., […]