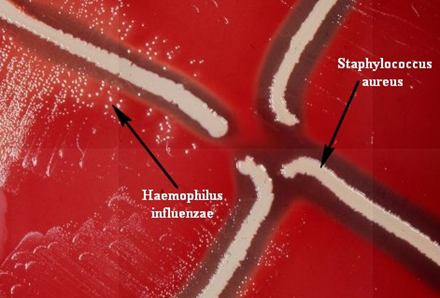
SATELLITISM TEST
Satellitism test is a culture-based test which is used to identify Haemophilus influenzae in the laboratory. Haemophilus influenzae is a fastidious bacterium that requires both X factor (haemin) and V factor (NAD or NADP) for growth. Blood agar lacking any of these growth factors will not support most strains of H. influenzae. When grown in […]