Bacillus anthracis
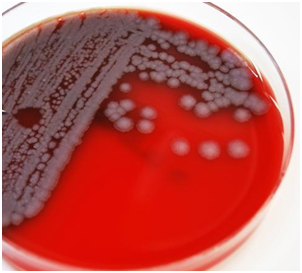
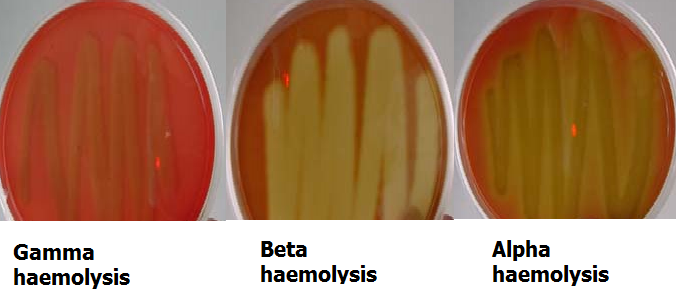
Bacillus anthracis is a mesophilic, Gram-positive, aerobic, catalase-positive, rod-like and spore-forming bacterium that causes anthrax in both humans and animals (e.g. goats, cattle and sheep). Due to their ubiquity in the soil, microbes in the genus Bacillus are often referred to as a normal flora of the soil. B. anthracis is very unique amongst other […]
Bacillus anthracis Read More »
Bacteriology