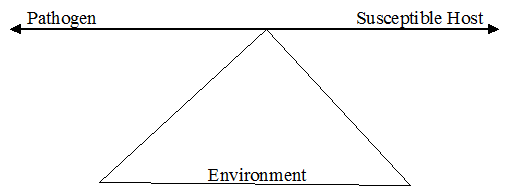
THE TRIANGLE OF EPIDEMIOLOGY (Epidemiological triad)
The characteristics of a disease are largely dependent on the relationship between the environment, the disease causing microorganism (pathogen) and a susceptible host. Health; it must be noted is a state of equilibrium or balance between susceptible host (the individual) and the agent (pathogenic microorganism). The features of host, environment, and agent (disease cause) are […]
THE TRIANGLE OF EPIDEMIOLOGY (Epidemiological triad) Read More »
Epidemiology