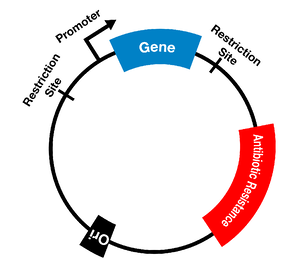
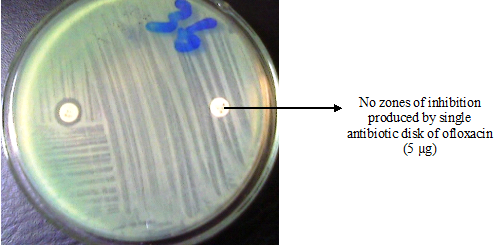
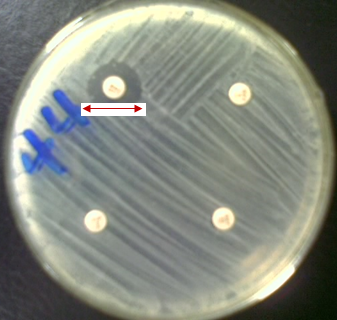
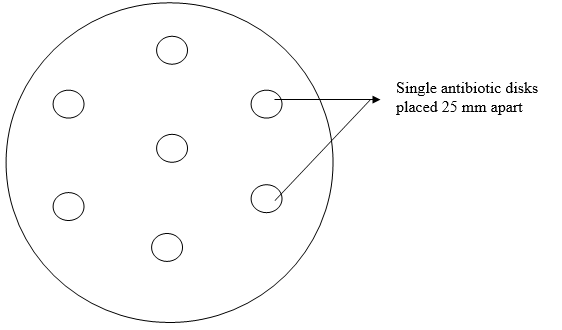
Genetic resistance of microbes to antibiotics is due to a chromosomal mutation in the bacterial […]
Tag: antibiotic resistance
Materials from the iAMR team for teaching & illustrating AMR
Are you looking for more information about Antibiotic Resistance or antimicrobial resistance (AMR)? Do you […]
TYPES OF ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
Bacteria have evolved to survive in diverse environments. They survive exposure to harsh chemicals including […]
ANTIMICROBIAL (ANTIBIOTIC) RESISTANCE: definition, selective pressure and clonal selection
Antibiotic or antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a phenomenon that occurs when bacteria are not killed […]
ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
Antibiotic resistance is a phenomenon that occurs when bacteria are not killed or inhibited by […]
PHENOTYPIC DETECTION METHODS OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE (AMR) IN PATHOGENIC BACTERIA
The expression “phenotypic” is from the word phenotype, which means “the observable characteristics of an […]