Are you looking for more information about Antibiotic Resistance or antimicrobial resistance (AMR)? Do you […]
Tag: antimicrobial resistance
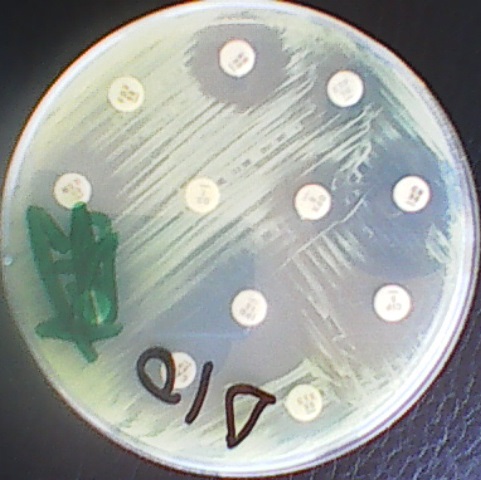
MULTIDRUG RESISTANT BACTERIA (MDRB)
The introduction of antibiotics into clinical medicine for the treatment of infectious diseases heralded an […]
FACTORS THAT CONTRIBUTE TO ANTIBIOTIC (ANTIMICROBIAL) RESISTANCE
Antibiotic resistance is a global health problem that bedevils our health sector and threatens our […]
ANTIMICROBIAL (ANTIBIOTIC) RESISTANCE: definition, selective pressure and clonal selection
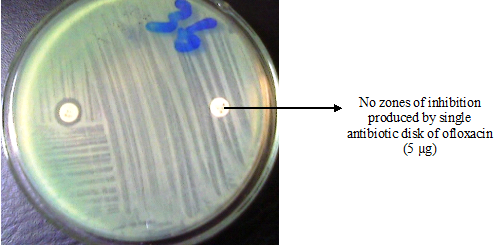
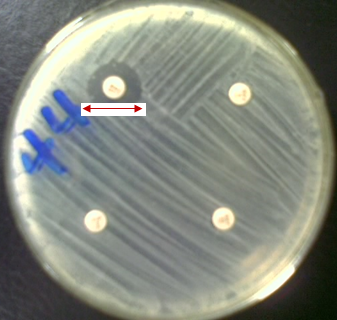
Antibiotic or antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a phenomenon that occurs when bacteria are not killed […]
WHO Global Principles for the Containment of Antimicrobial Resistance in Animals Intended for Food
Purpose: To minimize the negative public health impact of the use of antimicrobial agents in […]
ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
Antibiotic resistance is a phenomenon that occurs when bacteria are not killed or inhibited by […]
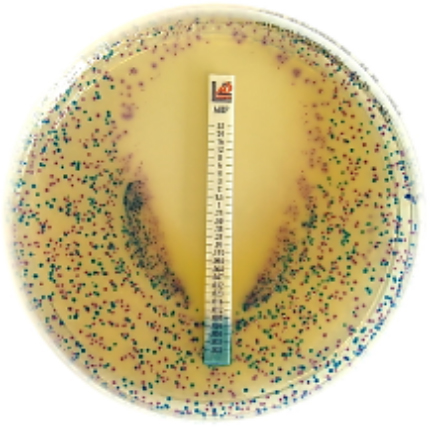
Chromogenic culture media for detecting antimicrobial resistance mechanisms
Chromatic Super CAZ/AVI Chromogenic medium for detecting Ceftazidime-avibactam resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Chromatic Super CAZ/AVI is […]
BRIEF HISTORY OF ANTIBIOTICS
Antibiotic history dates back to 1928 when Sir Alexander Fleming discovered the antibacterial effects of […]