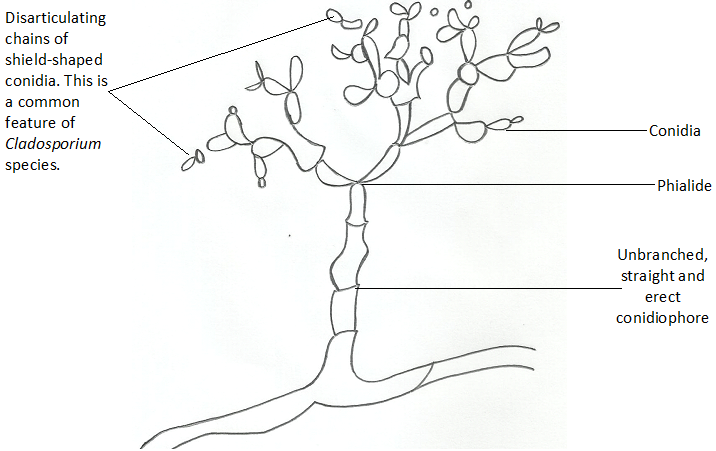
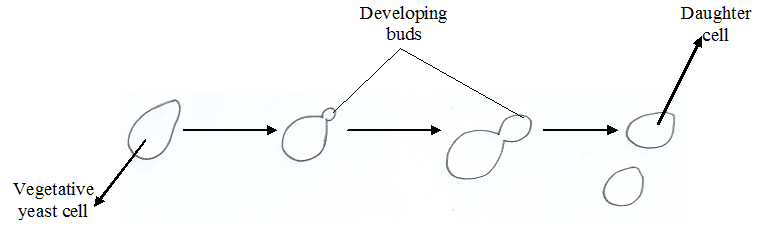
The spores (conidia) are produced in dry chains from the tips of the phialides, with […]
Tag: fungi
FUNGAL REPRODUCTION
Fungal reproduction is unique and distinct from those of other microbial cells such as bacteria. […]
SLIME MOULDS
Slime moulds are eukaryotic organisms that have fungus-like features as well as some animal- or […]
TAXONOMIC GROUPS OF MICROORGANISMS
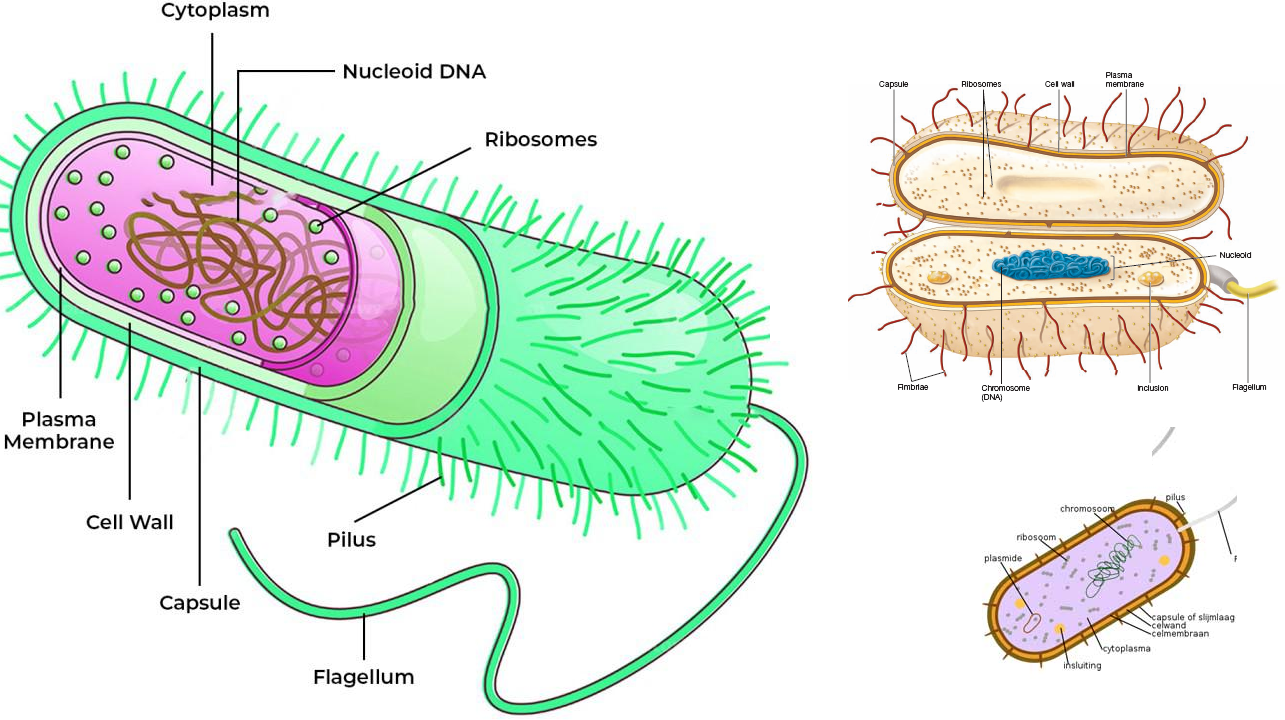
There are millions of microorganisms in the face of the planet earth, and these organisms […]
Introduction to Mycology
What is mycology? Mycology is simply defined as the study of fungi. Fungi (singular: fungus) […]