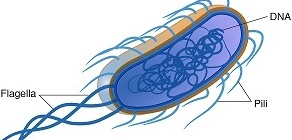
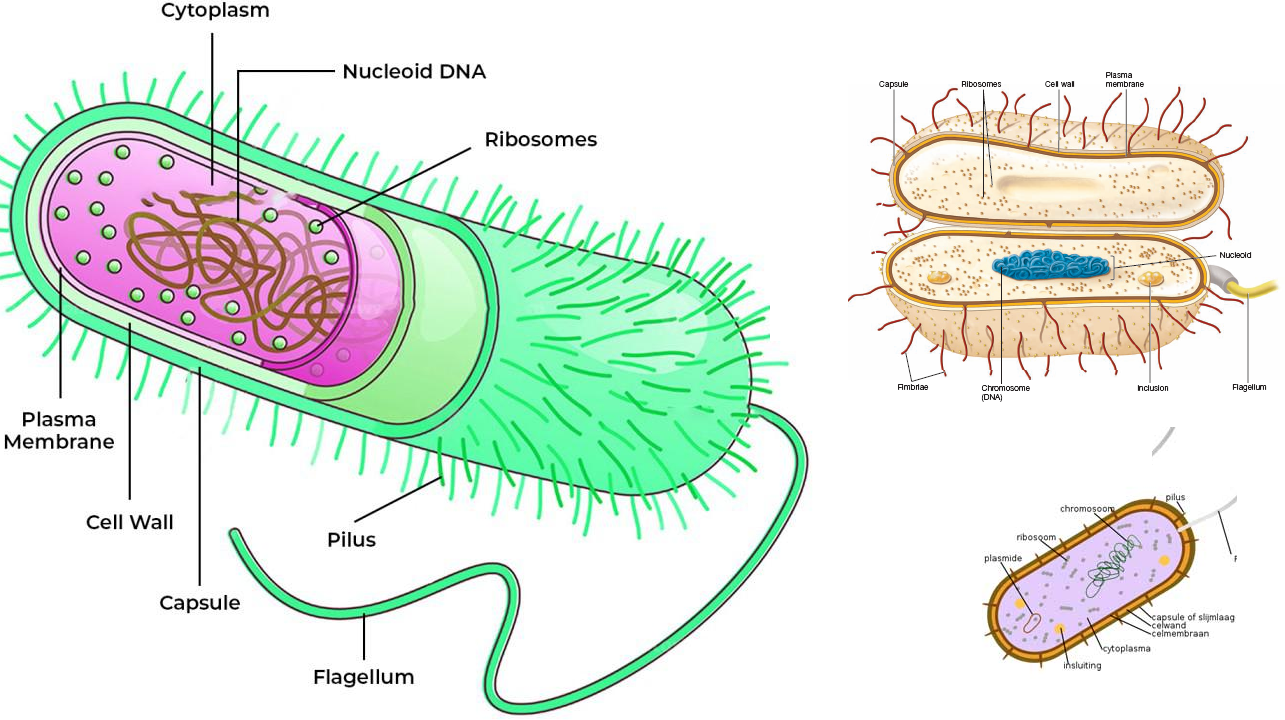
All bacterial cells are extremely infinitesimal (i.e. microscopic), and are never visible to the naked […]
Tag: bacteria
OVERVIEW OF BACTERIA
Bacteria (singular: Bacterium) is one of the two important members of the prokaryotes (i.e. cells […]
ARCHAEA, EUBACTERIA and BACTERIA
Archaea bacteria generally inhabit terrestrial and aquatic environments where the condition of living is extremely […]
MICROBIAL DIVERSITY: Archaea, Eubacteria, Bacteria
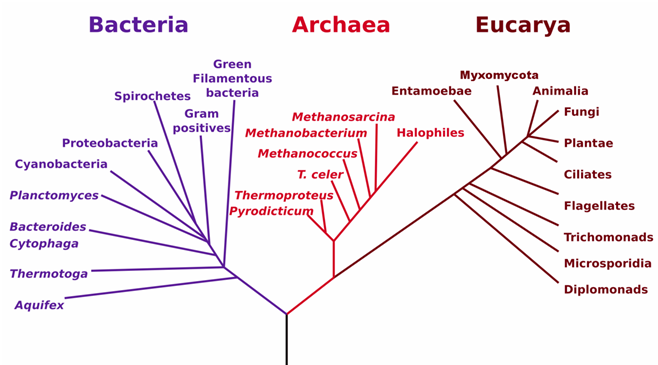
The phylogenetic tree of life comprises mainly of Eubacteria, Archaea and Bacteria. Eubacteria or Eukarya, […]
TAXONOMIC GROUPS OF MICROORGANISMS
There are millions of microorganisms in the face of the planet earth, and these organisms […]
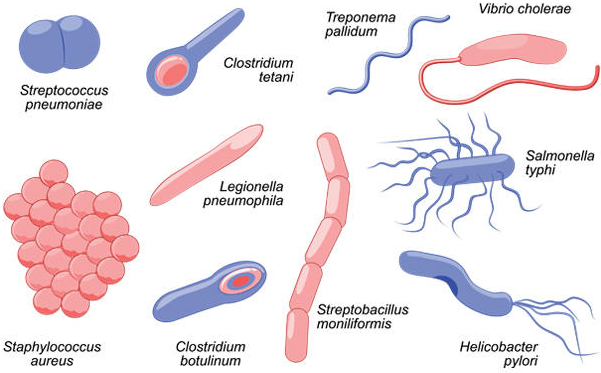
LIST OF SOME BACTERIA OF MEDICAL IMPORTANCE AND THEIR FEATURES
Bacillus cereus Gram-positive rods Motile organism Forms endospores Colonies are non-haemolytic on blood agar Aerobic […]
INTRODUCTION TO BACTERIOLOGY LAB
Bacteriology is simply defined as the scientific study of bacteria. Pathogenic bacteriology thus, is the […]
Introduction to (Medical) Bacteriology
Medical Bacteriologyis a branch of medical microbiology that is concerned with the diagnosis, prevention and […]