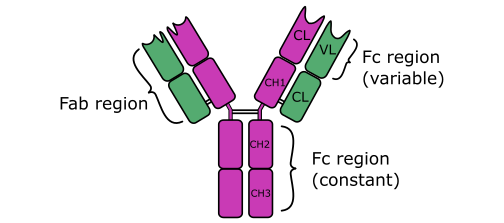
Immunoglobulin D (IgD) is an antibody with the basic four polypeptide structure of an immunoglobulin (Figure 1); and IgD is mostly found attached to the membranes of B cell. IgD is a membrane bound immunoglobulin, and it has a molecular weight (MW) of about 180, 000 DA.
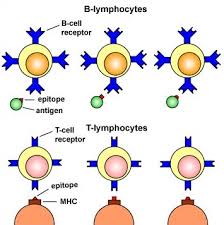
Immunoglobulin D is present in only trace amounts in serum; and in association with IgM, IgD is the main membrane-bound antibody commonly expressed on the surfaces of mature B cells or lymphocytes where they are believed to function as antigen receptors.
IgD does not fix complements, and it does not cross the placental barriers. IgD is absent from memory cells, and their full physiological function in the immune system is yet to be unraveled.
REFERENCES
Abbas A.K, Lichtman A.H and Pillai S (2010). Cellular and Molecular Immunology. Sixth edition. Saunders Elsevier Inc, USA.
Actor J (2014). Introductory Immunology. First edition. Academic Press, USA.
Alberts B, Bray D, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K and Walter P (1998). Essential Cell Biology: An Introduction to the Molecular Biology of the Cell. Third edition. Garland Publishing Inc., New York.
Bach F and Sachs D (1987). Transplantation immunology. N. Engl. J. Med. 317(8):402-409.
Barrett J.T (1998). Microbiology and Immunology Concepts. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven Publishers. USA.
Jaypal V (2007). Fundamentals of Medical Immunology. First edition. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd, New Delhi, India.
John T.J and Samuel R (2000). Herd Immunity and Herd Effect: New Insights and Definitions. European Journal of Epidemiology, 16:601-606.
Levinson W (2010). Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology. Twelfth edition. The McGraw-Hill Companies, USA.
Roitt I, Brostoff J and Male D (2001). Immunology. Sixth edition. Harcourt Publishers Limited, Spain.
Zon LI (1995). Developmental biology of hematopoiesis. Blood, 86(8): 2876–91.
Discover more from Microbiology Class
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.