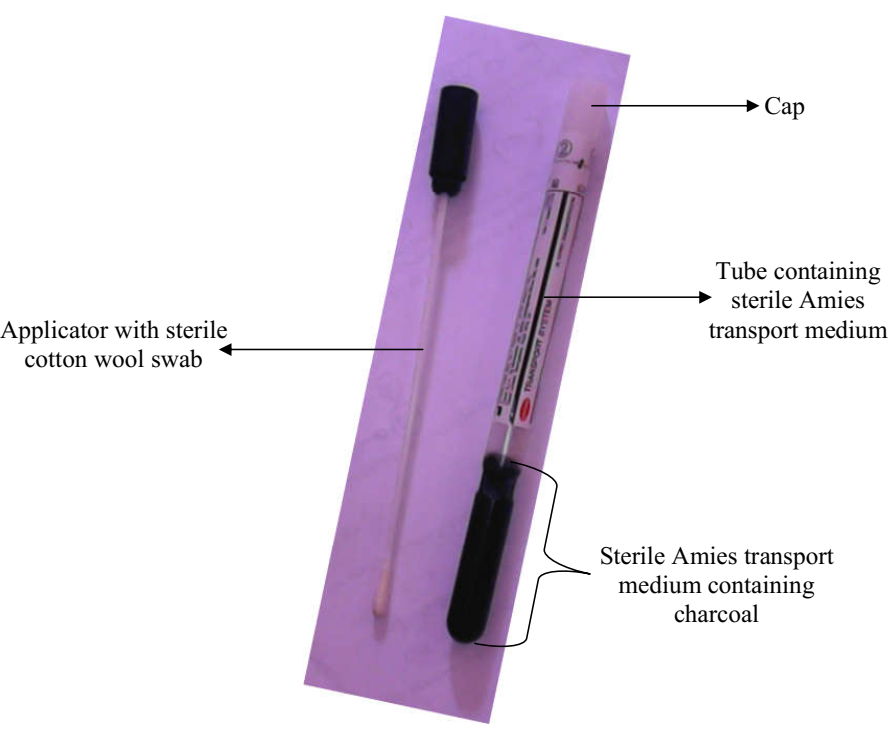
Good laboratory practice (GLP) is simply defined as a laboratory quality measure or protocol that is concerned with the organizational process and the conditions under which laboratory experimentations (inclusive of other non-clinical studies) are planned, performed, monitored, recorded, archived, retrieved and reported.
The main goal of GLP in any medical or non-medical laboratory is to help researchers carry out experiments anywhere and anytime and obtain results that are reliable, repeatable, auditable, and recognizable by researchers elsewhere.
GLP principles ensures that laboratory experimentations are conducted based on global best practices; and that the results generated from such experimentations are free from bias especially false-positive results and false-negative results.
It also covers all aspects that have to do with good laboratory facility equipped with adequate laboratory equipment for undertaking different laboratory procedures especially as it is peculiar to such laboratory.
GLP ensures that laboratory personnel are well trained and that adequate number of laboratory personnel is on ground o man the facility. In addition, GLP ensures that laboratory equipment and/or instruments are well maintained and routinely calibrated in order to ensure that the results or data that they generate are accurate and reliable.
It is the sole duty of laboratory personnel to ensure that the principles of GLP are adhered to at every point when research and other studies are undertaken within or outside the laboratory facility.
REFERENCES
Dubey, R. C. and Maheshwari, D. K. (2004). Practical Microbiology. S. Chand and Company LTD, New Delhi, India.
Garcia L.S (2010). Clinical Microbiology Procedures Handbook. Third edition. American Society of Microbiology Press, USA.
Garcia L.S (2014). Clinical Laboratory Management. First edition. American Society of Microbiology Press, USA.
Madigan M.T., Martinko J.M., Dunlap P.V and Clark D.P (2009). Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 12th edition. Pearson Benjamin Cummings Inc, USA.
Mahon C. R, Lehman D.C and Manuselis G (2011). Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology. Fourth edition. Saunders Publishers, USA.
Prescott L.M., Harley J.P and Klein D.A (2005). Microbiology. 6th ed. McGraw Hill Publishers, USA. Pp. 296-299.
Ryan K, Ray C.G, Ahmed N, Drew W.L and Plorde J (2010). Sherris Medical Microbiology. Fifth edition. McGraw-Hill Publishers, USA.
Salyers A.A and Whitt D.D (2001). Microbiology: diversity, disease, and the environment. Fitzgerald Science Press Inc. Maryland, USA.
Discover more from Microbiology Class
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.