Chromatic Super CAZ/AVI
Chromogenic medium for detecting Ceftazidime-avibactam resistant Gram-negative bacteria.
Chromatic Super CAZ/AVI is a selective and differential chromogenic medium used for screening ceftazidime-avibactam resistance in Enterobacterales and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chromatic Super CAZ/AVI is not intended to diagnose infection or guide therapy. Results can be interpreted after incubation for 18-24 hours. Subculture to a non-selective medium is required for confirming identification, antimicrobial susceptibility testing and epidemiological typing.
Chromatic Colistin
Chromogenic medium for detection of colistin-resistant organisms from clinical specimens and other materials.
Chromatic Colistin is a selective chromogenic medium used for the isolation and differentiation of Colistinresistant Gram-negative bacteria. The medium is intended for screening of faecal samples and can also be used to confirm colistin resistance of isolates from non-selective and non-chromogenic culture media.
Chromatic ESBL
Selective chromogenic medium for screening Gram-negative ESBL-producing bacteria.
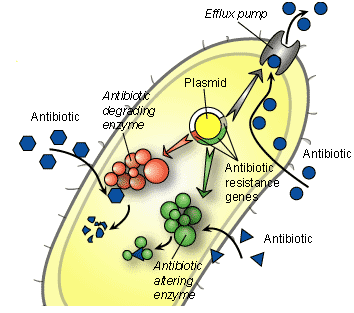
ESBL (Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamases) are enzymes that confer resistance to penicillins, extended-spectrum third generation cephalosporins (C3G) and monobactams. The ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae are responsible of severe hospital-acquired infections. The correct and early detection of ESBL-producing microorganisms is critical for addressing to the most appropriate antimicrobial therapy and avoiding the spread of infections. Chromatic ESBL medium contains a mixture of chromogenic compounds and antibiotics that allow the the growth of ESBL-producing bacteria while inhibit the other bacteria, including the ampC-positive. While the AmpC-positive bacteria can still be treated with certain beta-lactamase-stable antibiotics, the presence of an ESBL infection seriously limits treatment options because of the wide resistance acquired.
Chromatic CRE
Screening medium for the detection of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae.
Chromatic CRE contains a mixture of carbapenems for screening a wide variety of carbapenem-resistance mechanisms and provides presumptive identification of E. coli and the Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia and Citrobacter (KESC) group directly from clinical specimens.
Carbapenems, successfully used to treat multi-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections, including ESBL positive strains, are not efficacious against the Enterobacteriaceae resistant to carbapenems, thus generating a significant risk of hospital-acquired infections.
Chromatic OXA-48
Selective chromogenic medium for the screening of OXA-48 type Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae.
OXA-48 CRE are multi-resistant bacteria potentially responsible of hospital infections. The detection of OXA-48 CRE carriers by Chromatic OXA-48 can prevent and help surveil those infections.
Chromatic OXA-48, with its own proprietary formulation, includes antimicrobial agents and chromogenic substrata mixture that allows the selective growth of OXA-48 CRE and the identification of Escherichia coli (red color), Klebsiella spp. (Blue-violet), Enterobacter spp. (blue-green), Citrobacter spp. (blue with red halo).
Chromatic VRE
Chromogenic medium for screening vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
Chromatic VRE contains a mixture of antibiotics including vancomycin for screening Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and provides presumptive identification of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis directly from clinical specimens.
VRE have recently been recognized as one of the most severe cause of nosocomial infections.
An intrinsic resistance (vanC, vanD, vanE, vanF etc) is found in E. gallinarum and E. casseliflavus/E. flavescens and shows low resistance to vancomycin. Instead, an acquired resistance of vancomycin in enterococci (vanA & vanB types) is mostly detected in E. faecium and E. faecalis.
The prompt detection of Vancomycin-resistance of E. faecium and E. faecalis is basic for avoiding the spread of this resistance to more virulent such as S. aureus.
Chromatic MRSA
Selective chromogenic medium for isolating methicillin- resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) caused an increasing number of hospital infections in the recent years.
A wide range of antimicrobial compounds, including the beta-lactam antibiotics, result unsuccessful for treating the methicillin resistant S. aureus.
Chromatic MH
Chromogenic Muller Hinton for presumptive identification and susceptibility testing of various microorganisms from clinical specimens.
In the Intensive Care Unit the mortality rates for VAP, sepsis, surgical site or intra-abdominal, catheter related infections are critically high. Direct M.I.C. on CSF, positive blood culture bottles and other specimens from critical patients and direct M.I.C. on bronchial aspirates from patients with VAP can contribute with timely and essential information to save the life of patients.
Source:
Discover more from Microbiology Class
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.