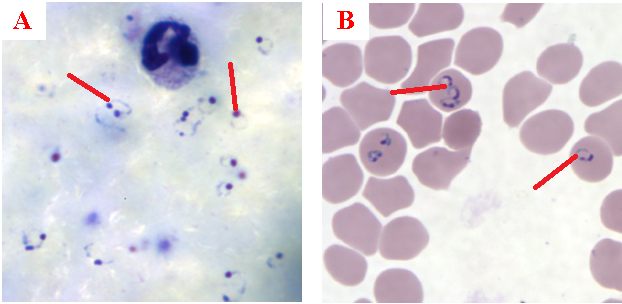
- Sporozoite: Sporozoite is the infectious form of Plasmodium parasite, which is injected into humans by the bite of female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- Merozoite: Merozoite is the form of the Plasmodium parasite that invades the red blood cells immediately after its release from the rupturing of schizonts in the liver cells.
- Oocyst: Oocyst is a stage of the Plasmodium parasite which is produced when male and female gametes combine within the mosquito.
- Gametes: Gametes are the reproductive elements of the Plasmodium parasite, and it is made up of the male and female forms.
- Gametocytes: Gametocytes are the precursors of the sexual forms of Plasmodium parasite, which are released as either male or female gametes within the gut or stomach of the mosquito.
- Microgametocytes: Microgametocytes are the male gametes of the Plasmodium parasite.
- Macrogametocytes: Macrogametocytes are the female gametes of the Plasmodium parasite.
- Haploid: Haploid cells are cells that contain a half set of the entire Plasmodium parasite chromosomes.
- Ookinete: Ookinete is the actively moving zygote form of the Plasmodium parasite that enters the stomach of the female Anopheles mosquito to form an oocyst under the outer lining of the mosquitoes’ gut. Ookinete is the zygote that is motile.
- Diploid: Diploid cells are cells that contain a full set of the Plasmodium parasitechromosomes.
- Zygote: Zygote is the diploid cell formed when the male gamete (microgametocyte) and a female gamete (macrogametocyte) fuse or join together.
References
Aschengrau A and Seage G.R (2013). Essentials of Epidemiology in Public Health. Third edition. Jones and Bartleh Learning,
Beers M.H., Porter R.S., Jones T.V., Kaplan J.L and Berkwits M (2006). The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy. Eighteenth edition. Merck & Co., Inc, USA.
Chiodini P.L., Moody A.H., Manser D.W (2001). Atlas of medical helminthology and protozoology. 4th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
Dictionary of Microbiology and Molecular Biology, 3rd Edition. Paul Singleton and Diana Sainsbury. 2006, John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Canada.
Ghosh S (2013). Paniker’s Textbook of Medical Parasitology. Seventh edition. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers,
Leventhal R and Cheadle R.F (2013). Medical Parasitology. Fifth edition. F.A. Davis Publishers,
Lucas A.O and Gilles H.M (2003). Short Textbook of Public Health Medicine for the tropics. Fourth edition. Hodder Arnold Publication, UK.
MacMahon B., Trichopoulos D (1996). Epidemiology Principles and Methods. 2nd ed. Boston, MA: Little, Brown and Company. USA.
Mandell G.L., Bennett J.E and Dolin R (2000). Principles and practice of infectious diseases, 5th edition. New York: Churchill Livingstone.
Molyneux, D.H., D.R. Hopkins, and N. Zagaria (2004) Disease eradication, elimination and control: the need for accurate and consistent usage. Trends Parasitol, 20(8):347-51.
Nelson K.E and Williams C (2013). Infectious Disease Epidemiology: Theory and Practice. Third edition. Jones and Bartleh Learning
Roberts L, Janovy J (Jr) and Nadler S (2012). Foundations of Parasitology. Ninth edition. McGraw-Hill Publishers, USA.
Schneider M.J (2011). Introduction to Public Health. Third edition. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Sudbury, Massachusetts, USA.
Discover more from Microbiology Class
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.