Sterility is central and important for the success of any industrial fermentation process. Industrial microbiology […]
Tag: sterilization
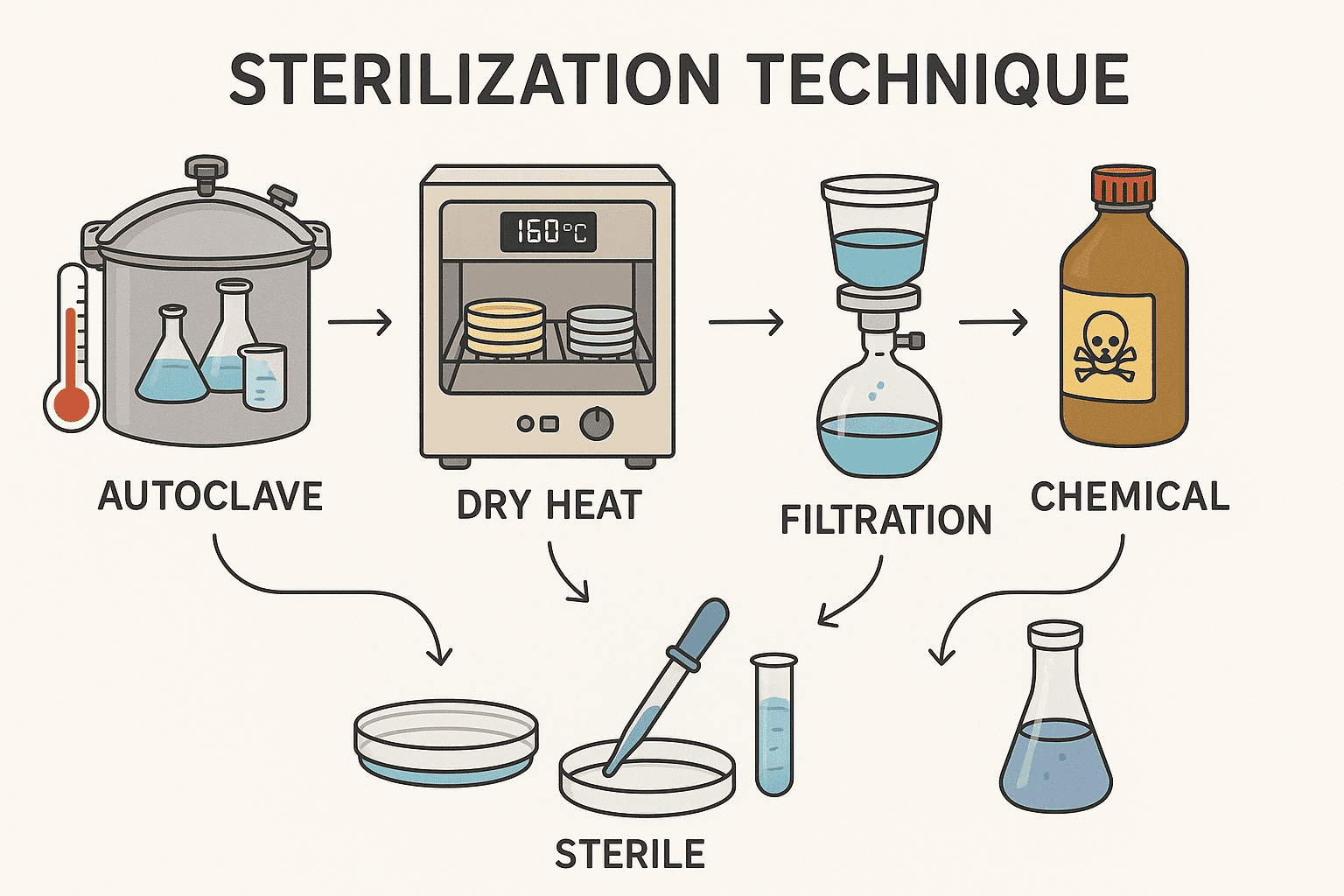
INCUBATION & STERILIZATION TECHNIQUE
Microorganisms are incubated in the incubator at different temperatures and time interval depending on the […]
Sterile & Non-Sterile Pharmaceutical Products
Sterile pharmaceutical products are defined as sensitive pharmaceutical products that should be free from living micro-organisms, […]
LOUIS PASTEUR (1822-1895)
Louis Pasteur, a French scientist was the first to report the role of microorganisms in […]