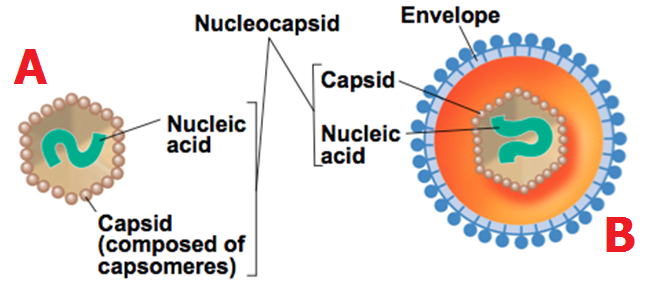
Though they are known to cause plethora of infectious diseases in man, plants and animals; viruses are very useful tools that can be exploited to the benefit of mankind.
- Vaccine Development and Production
Viruses are fundamental to the development of vaccines used in the prevention of infectious diseases. Vaccines may contain attenuated (weakened), inactivated, or recombinant viral components that stimulate protective immunity. Examples include vaccines against Poliomyelitis, Measles, Yellow fever, and Influenza. Viral vector technologies were also instrumental in the development of vaccines against COVID-19. These vaccines reduce morbidity and mortality, decrease healthcare expenditures, and prevent large-scale economic disruptions. Viral vaccines are equally important in veterinary medicine, where they protect livestock from economically devastating diseases.
- Bacteriophages in Bacterial Taxonomy (Phage Typing)
Bacteriophages (phages), viruses that infect bacteria, are used in bacterial classification through a method known as phage typing. In this technique, bacterial strains are differentiated based on their susceptibility to specific bacteriophages. Phage typing has been widely used in tracking outbreaks of pathogens such as Salmonella entericaand Staphylococcus aureus. This approach enhances epidemiological surveillance, supports outbreak investigation, and enables rapid containment of infectious diseases, thereby reducing public health and economic burdens.
- Development of Antiviral Drugs
The study of viral structure and replication mechanisms facilitates the development of antiviral drugs. For instance, research on Human immunodeficiency virus led to the production of antiretroviral therapies that significantly reduce mortality and improve quality of life. Similarly, investigations into Hepatitis C virus resulted in highly effective direct-acting antiviral agents. The antiviral pharmaceutical sector represents a major component of the global biotechnology and healthcare economy.
- Laboratory Diagnosis and Diagnostic Reagents
Viral components such as antigens, antibodies, and nucleic acids are used in the production of diagnostic tools for infectious diseases. Techniques including polymerase chain reaction (PCR), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and rapid antigen detection tests rely on viral materials. Accurate and early diagnosis improves disease management, supports surveillance programs, and minimizes economic losses associated with uncontrolled disease transmission.
- Biological Pest Control (Viral Biopesticides)
Certain viruses are used as environmentally friendly biological control agents in agriculture. Baculoviruses, such as Nucleopolyhedrovirus, are applied to control insect pests that damage crops. Viral biopesticides are highly host-specific, reducing harm to beneficial organisms and lowering dependence on chemical pesticides. This contributes to sustainable agriculture, improved crop yield, and reduced economic losses due to pest infestations.
- Phage Therapy in Antimicrobial Resistance Management
Bacteriophages are increasingly explored as therapeutic agents in phage therapy, particularly for treating infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria. As antimicrobial resistance continues to rise globally, phage-based therapeutics represent a promising and economically significant alternative to conventional antibiotics.
- Reverse transcriptase (RT) as a catalytic enzyme in molecular biology
Reverse transcriptase (RT) is a specialized DNA polymerase that catalyzes the synthesis of complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template. Biochemically, it is classified as an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase because its substrate is RNA rather than DNA. Unlike conventional DNA polymerases, RT does not require a DNA template; instead, it reads single-stranded RNA and synthesizes a complementary DNA strand in the 5′→3′ direction. Many RT enzymes also possess RNase H activity, which degrades the RNA strand of an RNA–DNA hybrid during cDNA synthesis, thereby facilitating second-strand DNA synthesis. This dual enzymatic capacity is critical for the replication cycle of certain viruses and has been extensively exploited in molecular biology.
- Occurrence of reverse transcriptase in retroviruses
Reverse transcriptase is predominantly produced by viruses belonging to the Retroviridae family, commonly known as retroviruses. Members of this family include well-known pathogens such as Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) and Human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV-1). Retroviruses possess single-stranded positive-sense RNA genomes. Upon entry into a susceptible host cell, the viral RT enzyme synthesizes a complementary DNA copy of the viral RNA genome. This newly formed viral DNA is subsequently integrated into the host genome by another viral enzyme, integrase. The integrated viral DNA, known as a provirus, becomes a permanent part of the host’s genetic material and can direct the production of new viral particles. This replication strategy fundamentally differs from that of DNA viruses and most RNA viruses and was a major conceptual breakthrough in molecular genetics.
- Application of reverse transcriptase in recombinant DNA technology
Reverse transcriptase has become indispensable in recombinant DNA technology and modern molecular biology. One of its principal applications is in the synthesis of complementary DNA (cDNA) libraries from messenger RNA (mRNA). Because eukaryotic genes contain introns that are removed during RNA processing, cDNA synthesized from mature mRNA represents only the coding (exonic) regions of genes. This property is particularly valuable when expressing eukaryotic genes in prokaryotic systems such as bacteria, which lack the machinery to remove introns. By generating cDNA from mRNA and inserting it into plasmid vectors, researchers can clone and express specific genes in host microorganisms for protein production.
- Role of RT in diagnostic and analytical techniques
Reverse transcriptase underpins several powerful diagnostic methodologies, most notably reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). In RT-PCR, viral or cellular RNA is first converted into cDNA using RT, and the cDNA is then amplified using DNA polymerase through the polymerase chain reaction. This approach enables the detection and quantification of RNA viruses, gene expression levels, and transcript variants with high sensitivity and specificity. Real-time RT-PCR (quantitative RT-PCR) has become a gold standard in clinical diagnostics, infectious disease surveillance, oncology, and gene expression studies. The enzyme’s ability to convert unstable RNA into stable DNA makes it central to transcriptomic analyses and molecular epidemiology.
- Viruses as vectors for gene transfer
Beyond their natural pathogenic roles, viruses can serve as highly efficient vectors for the transmission of genetic material between cells and organisms. Viral vectors are engineered viruses that have been modified to remove pathogenic genes while retaining their capacity to deliver therapeutic or experimental genes into target cells. Retroviral vectors, lentiviral vectors (derived from HIV), adenoviral vectors, and adeno-associated viral vectors are widely used in research and clinical gene therapy. The efficiency of viral entry, genome delivery, and, in some cases, stable integration into host DNA makes viruses uniquely suited for gene transfer applications.
- Mechanistic basis of viral vector utility
The effectiveness of viruses as vectors stems from their evolutionary optimization for cellular entry and genetic delivery. Viral surface proteins mediate attachment to specific host cell receptors, facilitating membrane fusion or endocytosis. Once inside the cell, the viral genome is transported to the nucleus (for DNA viruses and retroviruses) or remains in the cytoplasm (for many RNA viruses), where gene expression occurs. By replacing viral genes with therapeutic transgenes, scientists harness the virus’s natural delivery system while minimizing pathogenicity. This strategy has enabled advances in functional genomics, vaccine development, and gene therapy for inherited disorders.
- Viruses as anti-cancer agents (oncolytic viruses)
Some viruses have been deliberately employed as anti-cancer agents, a strategy known as oncolytic virotherapy. Oncolytic viruses are either naturally selective for tumor cells or genetically engineered to preferentially infect and lyse malignant cells while sparing normal tissues. Upon infecting cancer cells, these viruses replicate, induce cell lysis, and release progeny virions that can infect adjacent tumor cells. Additionally, tumor cell lysis releases tumor-associated antigens, which can stimulate anti-tumor immune responses. This dual mechanism direct oncolysis and immune activation makes oncolytic viruses a promising modality in cancer therapy.
- Clinical translation of oncolytic virotherapy
The clinical relevance of oncolytic viruses is exemplified by agents such as Talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC), an engineered herpes simplex virus approved for the treatment of advanced melanoma. T-VEC is modified to selectively replicate in tumor cells and to express granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), thereby enhancing anti-tumor immunity. Such therapeutic applications demonstrate how viruses, once viewed solely as pathogens, can be repurposed as precision biological tools in oncology and molecular medicine.
- Contribution of virology to cell and molecular biology
The study of viruses, particularly at the molecular level, has profoundly influenced the development of cell biology and molecular biology. Investigations employing cell and tissue culture techniques allowed scientists to propagate viruses in controlled environments, facilitating detailed analysis of viral replication cycles. Electron microscopy provided high-resolution visualization of viral structure, morphology, and host-cell interactions. Through these methodologies, virologists elucidated fundamental processes such as DNA replication, transcription, translation, RNA splicing, and intracellular trafficking.
- Discovery of key cellular and metabolic components through viral research
Research on viruses has led to the discovery of critical cellular enzymes, regulatory pathways, and genetic mechanisms. For example, the identification of reverse transcriptase revolutionized understanding of genetic information flow, challenging the classical “central dogma” of molecular biology. Studies of tumor viruses contributed to the discovery of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, illuminating the molecular basis of cancer. Similarly, investigations into viral-host interactions revealed mechanisms of immune evasion, apoptosis regulation, and signal transduction. These insights have clarified the molecular underpinnings of numerous infectious and non-infectious diseases.
- Impact on understanding molecular and infectious diseases
By dissecting viral replication and pathogenesis, scientists have gained a deeper understanding of how genetic and metabolic dysregulation leads to disease. Viral models have been instrumental in elucidating mechanisms of chronic infection, immune suppression, and malignant transformation. The integration of virology with genomics, proteomics, and structural biology continues to expand knowledge of host–pathogen interactions. Consequently, the molecular study of viruses has not only advanced basic biological science but has also provided diagnostic tools, therapeutic strategies, and preventive measures that address major human diseases.
In general, viruses have considerable economic importance in medicine, agriculture, biotechnology, and public health as aforesaid. Their applications contribute to disease prevention, outbreak control, pharmaceutical innovation, food security, and sustainable agricultural practices.
References
Acheson N.H (2011). Fundamentals of Molecular Virology. Second edition. John Wiley and Sons Limited, West Sussex, United Kingdom.
Alan J. Cann (2005). Principles of Molecular Virology. 4th edition. Elsevier Academic Press, Burlington, MA, USA.
Alberts B, Bray D, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts Kand Walter P (1998). Essential Cell Biology: An Introduction to the Molecular Biology of the Cell. Third edition. Garland Publishing Inc., New York.
Black, J.G. (2008). Microbiology: Principles and Explorations (7th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: J. Wiley & Sons.
Brian W.J Mahy and Mark H.C van Regenmortel (2010). Desk Encyclopedia of Human and Medical Virology. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, USA.
Brooks G.F., Butel J.S and Morse S.A (2004). Medical Microbiology, 23rd edition. McGraw Hill Publishers. USA.
Dimmock N (2015). Introduction to Modern Virology. Seventh edition. Wiley-Blackwell, New Jersey, United States.
Dimmock N.J, Easton A.J and Leppard K.N (2001). Introduction to modern virology. 5th edition. Blackwell Science publishers. Oxford, UK.
Discover more from Microbiology Class
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.