The central framework of molecular biology otherwise known as the “central dogma” is the starting […]
Category: Molecular Microbiology
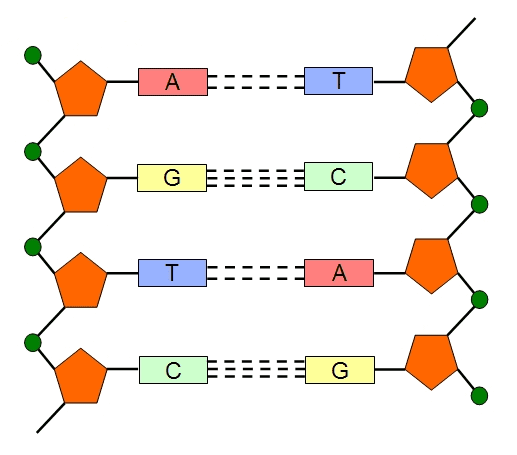
GENOMIC DNA
Genomic DNA is a double helix structure that is composed of several components including purines […]
Overview of Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the study of the genetic makeup of organisms at the level of […]
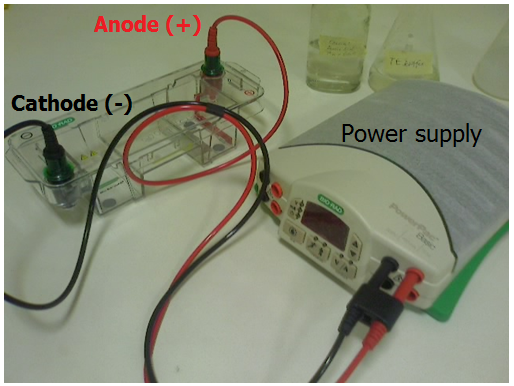
GEL ELECTROPHORESIS TECHNIQUE
The term “electrophoresis” refers to the movement of a solid particle (e.g. nucleic acids) through […]
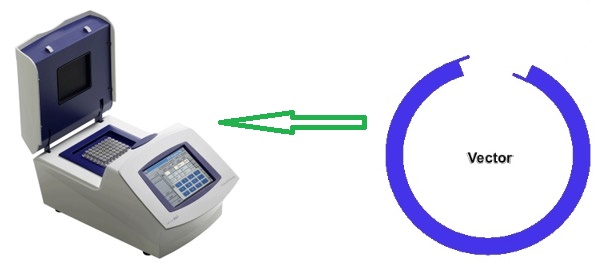
Introduction to Recombinant DNA (rDNA) Technology / Genetic Engineering
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology or genetic engineering is the in vitro controlled manipulation of nucleic […]