- They make a healthy human being to be less susceptible to pathogens.
- They help in stimulating the immune system against pathogens.
- They prevent the invasion and colonization of pathogens in and on the body.
- They provide protection against infections on the sites of the body (internal or external) they are located.
- They prevent pathogens from colonizing certain parts of the human body. For example, Lactobacillus acidophilus, a resident microflora of the vagina of women produces lactic acid from the fermentation of glycogen. This maintains a weakly acidic environment that prevents pathogens like Candida albicans and other aerobic bacteria from colonizing the adult female vagina.They also prevent the adhesion of pathogens on the human skin and other parts of the body including the mucosal surfaces.
- Intestinal microbial flora produces vitamin B12 and vitamin K (which are not manufactured by humans) in the gut.
- Intestinal microbial flora helps in the production of organic acids and gases (known as flatus) in the gut of humans and animals.
- They inhibit the growth of pathogens in the body by producing chemical substances that antagonizes the activities of the invading microbe.
- Normal microflora produces important vitamins in the body such as cobalamin (vitamin B12) in the gut. They are also believed to stimulate the immune system by producing certain natural antibodies that fights invading antigens.
- Knowledge on the microbiota found in and on different parts of the body helps a microbiologist to be acquainted with the likely infection/disease that will develop in a particular body site and, the type of microorganism to anticipate from the culture of specimens from such body locations.
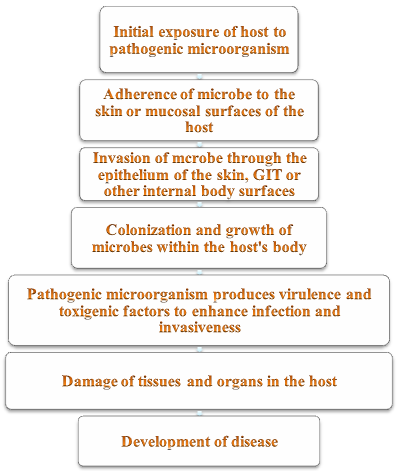
After exposure to an infectious agent, the body becomes contaminated by the agent, and the pathogenic microorganism eventually develops disease or infection in the susceptible human or animal host following a defined pattern (Figure 1). It is the duty of clinical microbiologists to isolate and characterize the infecting pathogenic microorganism(s), and differentiate same from normal microflora so that the appropriate treatment can be administered in order to restore the host to its normal working condition prior to its invasion by the pathogen.
References
Black, J.G. (2008). Microbiology: Principles and Explorations (7th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: J. Wiley & Sons.
Brooks G.F., Butel J.S and Morse S.A (2004). Medical Microbiology, 23rd edition. McGraw Hill Publishers. USA.
Champoux J.J, Neidhardt F.C, Drew W.L and Plorde J.J (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology: An Introduction to Infectious Diseases. 4th edition. McGraw Hill Companies Inc, USA.
Dictionary of Microbiology and Molecular Biology, 3rd Edition. Paul Singleton and Diana Sainsbury. 2006, John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Canada.
Engleberg N.C, DiRita V and Dermody T.S (2007). Schaechter’s Mechanisms of Microbial Disease. 4th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, USA.
Gladwin M and Trattler B (2006). Clinical Microbiology Made Ridiculously Simple. 3rd edition. MedMaster, Inc., Miami, USA.
Levinson W (2010). Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology. Twelfth edition. The McGraw-Hill Companies, USA.
Madigan M.T., Martinko J.M., Dunlap P.V and Clark D.P (2009). Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 12th edition. Pearson Benjamin Cummings Inc, USA. Pp. 902-903.
Mahon C. R, Lehman D.C and Manuselis G (2011). Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology. Fourth edition. Saunders Publishers, USA.
Mandell G.L, Bennett J.E, Dolin R, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 5th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone, 2002.
Murray P.R, Baron E.J, Jorgensen J.H., Pfaller M.A and Yolken R.H (2003). Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 8th edition. Volume 2. American Society of Microbiology (ASM) Press, Washington, D.C, U.S.A.
Murray P.R., Rosenthal K.S., Kobayashi G.S., Pfaller M. A. (2002). MedicalMicrobiology. 4th edition. Mosby Publishers, Chile.
Discover more from Microbiology Class
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.