Microbiology as a field in the biological sciences saw the light of the day because […]
Category: General Microbiology
WHAT IS MICROBIOLOGY?
MICROBIOLOGY is simply defined as the study of microorganisms. Microorganisms or microbes are organisms that […]
Exploring Careers in Microbiology: What Microbiologists Do and Where They Work!
A guide to discovering diverse career paths through the world of microbes—from healthcare to climate […]
Overview of Microbiology
Microbiology (Micros-Small, Bios-Life, Logy-Study)is simply defined as the study of microscopic organisms that are too […]
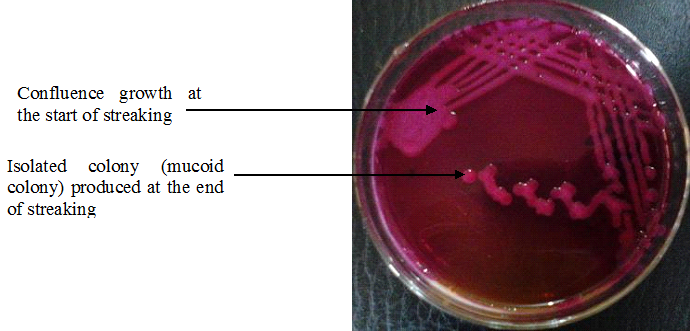
Colonial morphology of microorganisms
Microorganisms produce definite patterns on culture media plates as they grow and divide. These specific […]
Microbial Growth
Growth is simply defined as an irreversible increase in the size of an organism. It […]
Introduction to (Medical) Bacteriology
Medical Bacteriologyis a branch of medical microbiology that is concerned with the diagnosis, prevention and […]