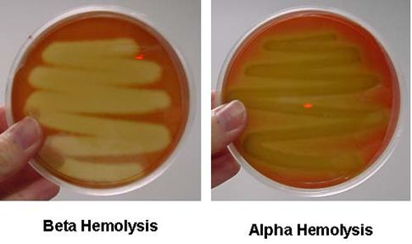
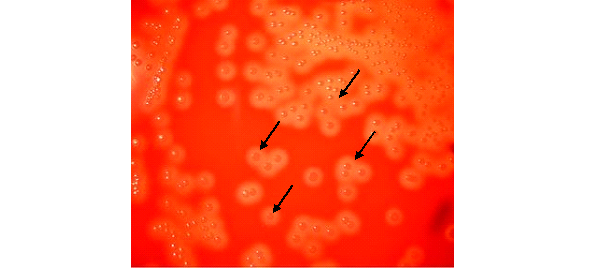
Streptococcus pneumoniae, prevalent in the human upper respiratory tract, causes various infections including pneumonia, often in vulnerable individuals. Its virulence is linked to its polysaccharide capsule, interfering with phagocytosis. Early detection and treatment with appropriate antibiotics and preventive vaccination are vital, especially for high-risk groups like the elderly and immunocompromised individuals.
Tag: streptococcus
STREPTOCOCCUS PYOGENES
Streptococcus pyogenes, a Group A Streptococcus, is a Gram-positive bacterium causing pharyngitis and various streptococcal diseases like scarlet fever, cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis. It produces numerous virulence factors including streptolysins and exotoxins. Diagnosis involves cultural, microscopic, and serological tests. Treatment includes antibiotics like penicillin, and no vaccines exist currently.
Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB): Key Microorganisms in Fermentation and Food Biotechnology
Introduction Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) constitute a diverse and functionally significant group of Gram-positive, non-sporulating, […]
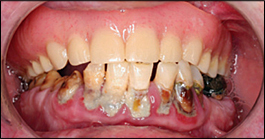
DENTAL CARIES
Dental caries is simply defined as the decaying of the teeth. It can also be […]